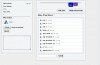
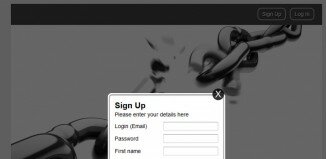
ExampleAn HTML form with two input fields and one submit button: |
Browser Support |
1. Definition and Usage
The <form> tag is used to create an HTML form for user input.
The <form> element can contain one or more of the following form elements:
An HTML form is used to pass data to a server.
Tip: The <form> element is a block-level element, and browsers create a line break before and after a form.
2. Differences Between HTML 4.01 and HTML5
HTML5 has added two new attributes: autocomplete and novalidate, and removed the accept attribute.
3. Differences Between HTML and XHTML
In XHTML, the name attribute is deprecated. Use the global id attribute instead.
4. Required Attributes
DTD indicates in which HTML 4.01/XHTML 1.0 DTD the attribute is allowed. S=Strict, T=Transitional, and F=Frameset.
| Attribute | Value | Description | DTD |
|---|---|---|---|
| action | URL | Specifies where to send the form-data when a form is submitted | STF |
5. Optional Attributes
| Attribute | Value | Description | DTD |
|---|---|---|---|
| accept | MIME_type | Specifies the types of files that the server accepts (that can be submitted through a file upload) | STF |
| accept-charset | character_set | Specifies a list of character encodings that the server accepts | STF |
| enctype | application/x-www-form-urlencoded multipart/form-data text/plain |
Specifies how the form-data should be encoded when submitting it to the server (only for method="post") | STF |
| method | get post |
Specifies the HTTP method to use when sending form-data | STF |
| name | name | Specifies the name of a form | TF |
| target | _blank _self _parent _top framename |
Deprecated. Specifies where to display the response that is received after submitting the form | TF |
6. Standard Attributes
The <form> tag supports the Standard Attributes in HTML.
7. Event Attributes
The <form> tag also supports the Standard Event Attributes in HTML.