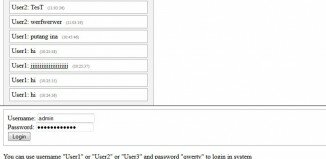
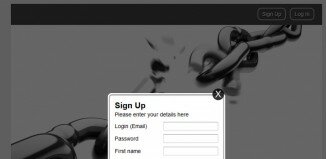
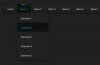
ExampleAn HTML form with three input fields; two text fields and one submit button: |
Browser Support |
1. Definition and Usage
The <input> tag is used to select user information.
<input> elements are used within a <form> element to declare input controls that allow users to input data.
An input field can vary in many ways, depending on the type attribute.
2. Tips and Notes
Tip: Use the <label> tag to define labels for <input> elements.
3. Differences Between HTML and XHTML
In HTML, the <input> tag has no end tag.
In XHTML, the <input> tag must be properly closed, like this <input />.
4. Optional Attributes
DTD indicates in which HTML 4.01/XHTML 1.0 DTD the attribute is allowed. S=Strict, T=Transitional, and F=Frameset.
| Attribute | Value | Description | DTD |
|---|---|---|---|
| accept | audio/* video/* image/* MIME_type |
Specifies the types of files that the server accepts (only for type="file") | STF |
| align | left right top middle bottom |
Deprecated. Use styles instead. Specifies the alignment of an image input (only for type="image") |
TF |
| alt | text | Specifies an alternate text for an image (only for type="image") | STF |
| checked | checked | Specifies that an <input> element should be preselected when the page loads (for type="checkbox" or type="radio") | STF |
| disabled | disabled | Specifies that an <input> element should be disabled | STF |
| maxlength | number | Specifies the maximum number of characters allowed in an <input> element | STF |
| name | name | Specifies the name of an <input> element | STF |
| readonly | readonly | Specifies that an input field should be read-only | STF |
| size | number | Specifies the width, in characters, of an <input> element | STF |
| src | URL | Specifies the URL of the image to use as a submit button (only for type="image") | STF |
| type | button checkbox file hidden image password radio reset submit text |
Specifies the type of <input> element | STF |
| value | text | Specifies the value of an <input> element | STF |
5. Standard Attributes
The <input> tag supports the following standard attributes:
| Attribute | Value | Description | DTD |
|---|---|---|---|
| accesskey | character | Specifies a keyboard shortcut to access an element | STF |
| class | classname | Specifies a classname for an element | STF |
| dir | rtl ltr |
Specifies the text direction for the content in an element | STF |
| id | id | Specifies a unique id for an element | STF |
| lang | language_code | Specifies a language code for the content in an element | STF |
| style | style_definition | Specifies an inline style for an element | STF |
| tabindex | number | Specifies the tab order of an element | STF |
| title | text | Specifies extra information about an element | STF |
| xml:lang | language_code | Specifies a language code for the content in an element, in XHTML documents | STF |
6. Event Attributes
The <input> tag supports the following event attributes:
| Attribute | Value | Description | DTD |
|---|---|---|---|
| onblur | script | Script to be run when an element loses focus | STF |
| onchange | script | Script to be run when an element change | STF |
| onclick | script | Script to be run on a mouse click | STF |
| ondblclick | script | Script to be run on a mouse double-click | STF |
| onfocus | script | Script to be run when an element gets focus | STF |
| onmousedown | script | Script to be run when mouse button is pressed | STF |
| onmousemove | script | Script to be run when mouse pointer moves | STF |
| onmouseout | script | Script to be run when mouse pointer moves out of an element | STF |
| onmouseover | script | Script to be run when mouse pointer moves over an element | STF |
| onmouseup | script | Script to be run when mouse button is released | STF |
| onkeydown | script | Script to be run when a key is pressed | STF |
| onkeypress | script | Script to be run when a key is pressed and released | STF |
| onkeyup | script | Script to be run when a key is released | STF |
| onselect | script | Script to be run when an element is selected | STF |